The corneal tissue has several characteristics that make storage and transplantation easier, and the eye bank plays an important role in the whole process of corneal retrieval, storage and transplantation.
A compatible graft cornea tissue can restore or improve vision if you have a damaged or diseased cornea.
It is also called corneal grafting is a surgical procedure in which the damaged or diseased cornea of a person is replaced by a healthy and fresh cornea from another person.
1. Penetrating Keratoplasty (full thickness cornea grafting)
2. Lamellar Keratoplasty (partial thickness cornea grafting) anterior or posterior lamella
Corneal transplantation or Keratoplasty is the most commonly performed and also the most successful grafting technique used worldwide. Its success rate depends upon acceptance and rejection of the graft. Almost 10% of corneal grafts show tissue rejection.
In 1905, Dr. Eduard Zim performed the first corneal surgery and had success, and it was the first of any kind of transplant surgery. Today, keratoplasty is considered the most often performed and most successful organ transplantation technique worldwide.
The success of this surgical procedure has not been an easy going path.
In 1813 K Himly suggested replacing the opaque human cornea with another animal.
1824 F Reisinger suggested replacing the opaque human cornea with the clear animal cornea and termed this.
1910- 1950- VP Filatov known as father of Keratoplasty studied systematics of Keratoplasty suggested use of cornea as a donor tissue.
1974- Development of corneal storage media. Tudor Thomas, a clinical teacher, conceived the idea of a donor system for corneal grafts and an eye bank was established in East Grinstead in 1955.
1. Optical: To improve visual sharpness by replacing the damaged host tissue by clear healthy donor cornea tissue.
2. Reconstructive: To preserve corneal integrity in patients with stromal thinning and ectasia.
3. Therapeutic: To remove inflamed corneal tissue unresponsive to treatment by antibiotics.
• Fuchs' dystrophy, which is a degeneration of the innermost layer of the cornea- it's a hereditary condition.
• Keratoconus- a cornea that bulges out.
• Lattice dystrophy
• A thinning or tearing of the cornea
• Cornea scarring, clouding or swelling caused by an injury or infection
• A corneal ulcer, which is often caused by trauma, such as a scratched cornea
• Complications caused by previous eye surgery.
A thorough eye exam for conditions that might cause complications after surgery.
• Measurements of your eye doctor determine what size donor cornea you need.
• A review of all medications and supplements Treatment for other eye problems.
• Need to treat those problems before your surgery.
Surgical procedure for cornea grafting
Keratoplasty can be done by following procedures
Endothelial keratoplasty (EK)-
In this type of corneal grafting, the innermost layer of the cornea is replaced by the surgeon with a fresh and opaque corneal tissue. It is performed on those people who have corneal endothelial disorder or deterioration and conditions which damage endothelial tissues. In this type of surgery, air or gas bubbles are used to hold or push the fresh endothelial tissue within the underlying corneal tissue, which will support the corneal tissue.
DALK DEEP ANTERIOR LAMELLAR KERATOPLASTY (DALK)
As we know cornea has five thin layers, in this kind of corneal grafting, surgeon removes four layers leaving behind the fifth one. In this technique, the eye doctor injects air to lift the corneal layers and separates the outer layers of the cornea. Then the surgeon removes and replaces these layers. DALK is the most common procedure for people with corneal scars and keratoconus. Healing time is shorter in this type as compared to other keratoplasty procedure.
PENETRATING KERATOPLASTY-
Also called as full thickness transplant.
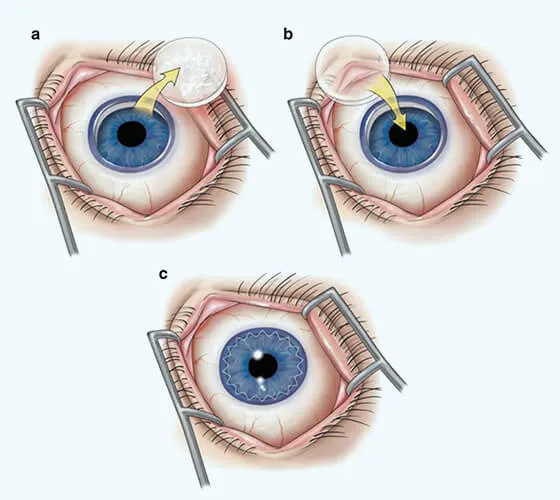
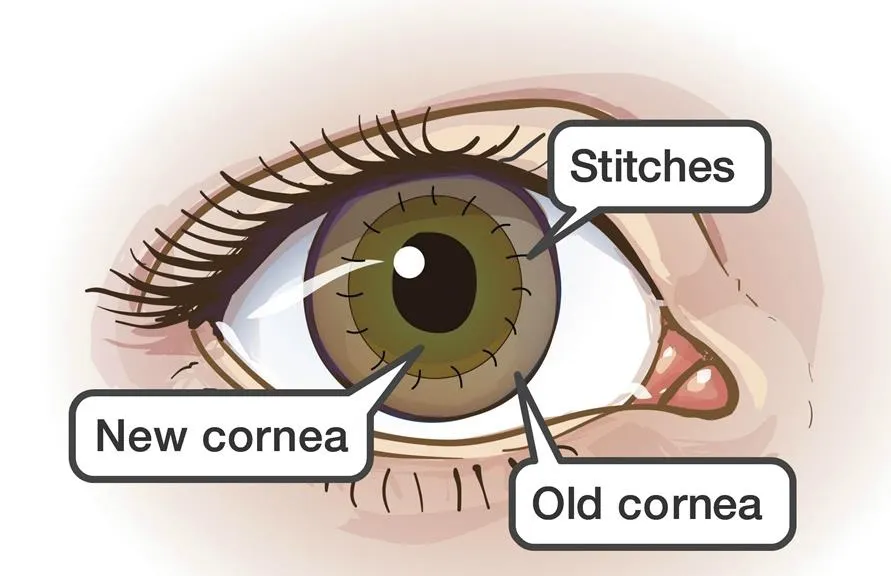
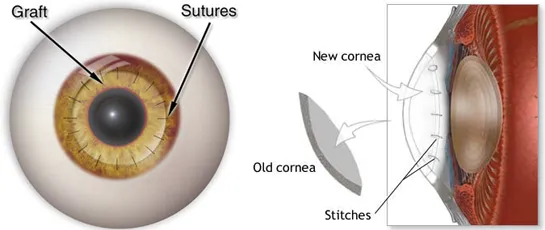
In this surgical method, the whole damaged cornea is replaced by compatible fresh tissue from the donor. The cornea is held from different places or corners with 16 or more stitches. This is carried out if the patient has a DALK transplant and it hasn't worked and also has damaged stromal and corneal layers. After the surgery, stitches should not be removed for almost 3 months. Vision improves as healing proceeds. A special instrument is used to make this precise circular cut.
The donor cornea, cut to fit, is placed in the opening. Your surgeon then uses stitches (sutures) to stitch the new cornea into place. The stitches might be removed at a later visit with an eye doctor.
Artificial cornea transplant (Keratoprosthesis) -
In some cases, if people aren't eligible for a cornea transplant from a donor cornea, they might receive an artificial cornea (Keratoprosthesis).
1. Risks are similar to other interocular procedures but it also includes some other complications which include graft rejection, detachment or displacement of lamellar transplants and primary graft failures.
2. Also have risk of infection, as cornea doesn't have blood vessels, it heals very slowly, the wound or cut can cause for infection with microbes, so antibiotic prophylaxis is prescribed.
3. Bleeding in eyes in severe case.
4. Retinal problems like retinal detachment and swelling.
5. Increase in eyeball pressure causing glaucoma.
Corneal grafting is a smooth surgical procedure, usually takes 2 hours and its success depends upon corneal acceptance and rejection. Corneal transplants can improve eye vision significantly or may it not work that well. So another surgery has to be followed in case of failure.
1. Contact lenses may help remove the need for corneal grafting in corneal disorders.
2. Phototherapeutic keratectomy
3. Corneal collagen cross linking
Corneal grafting or transplantation is essentially the first transplantation that ever took place.
| Week-Days: | 9am - 6pm |
| Sunday: | CLOSED |
Copyright © 2022 · All Rights Reserved Bharti Eye Foundation