
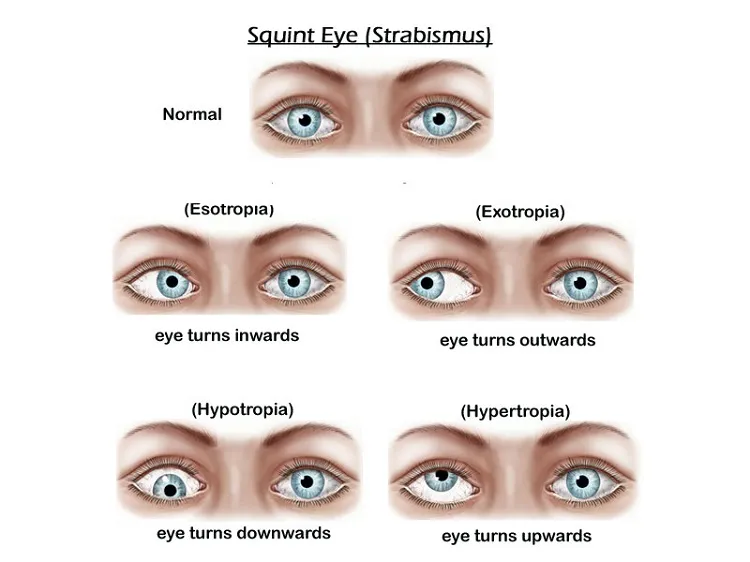
Our eye movement is controlled by six ocular muscles. Two muscles move the eye up to down, two left and right, and two help in the rotational movement of our eyes. When eye muscles are acting normally, our eyeballs can keep the focus on a particular spot together. However, when ocular muscle functioning is impaired, the eyes do not move with coordination. This is called squint or strabismus.
The squint (Misalignment) can be Convergent ( inwards) , Divergent (outwards) or Horizontal (Up or Down).
Sometimes squint occurs due to disorders in the brain.
Squint also makes binocular vision difficult as well, which means it's difficult for a person to appreciate depth or distance of an object called stereopsis

• Congenital means that a person is born with this disorder. Damage to the retina in premature babies or a tumour near the eye.
• Hereditary: if a gene is associated with or linked to a disorder i.e. Down syndrome
• Squinting develops when there is a problem with the control and functioning of six ocular muscles. This problem may be any kind of issue with the associated nerves and brain parts that control extraocular muscles.
• Various eye conditions like myopia, hypermetropia, and astigmatism. Disorders like cerebral palsy (impaired muscle coordination), brain tumors, or hydrocephalus(fluid in the brain) also lead to squinting.
• Some kinds of viral infections like measles can trigger squint.
Early diagnosis and detection are very important. From the age of three months to three years, the child's eyes must be examined. If there is need of glasses, it should be prescribed at the earliest. A child with a family history of amblyopic eyes should get their eyesight checked even before the age of three months. Tests that should be taken for squint eye are supposed to take care of retinal examination, corneal light reflex, and vision.
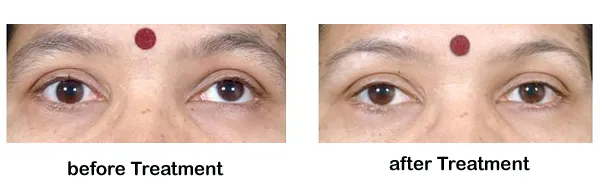
If squint is properly diagnosed and treated, this will prevent further complications such as lazy or amblyopic eye. Squint treatment is essential as it may lead to hampering one's professional life and confidence level. Various treatment options are considered for strabismus depending upon the severity of the squint, the individual, and the kind of squint.
• Treating lazy eye ( amblyopia)
• Wear glasses to correct any refractive errors in either or both eyes.
A child diagnosed with squint has to be properly examined.
Vision, need for glasses (refractive error) and a complete eye examination is necessary. The spectacle power and degree of squint will be examined until adulthood. If any residual squint remains with eyeglasses, it must be corrected surgically. The lazy eye is to be treated by patching or occluding the good eye or with Orthoptek exercises which is a new development in developing the stimulation of Macula ( the best seeing part of the eye). This will help weaker eyes focus on visual activities such as reading and color identification while the patch is on.
Squint surgery is required when all conservative methods of treatment are not able to correct it.
The success rate of squint surgery is very high in good hands. The patient will undergo a comprehensive eye and physical examination before the eye muscle surgery. The doctor will also take some eye measurements to determine which muscles are stronger or weaker. To treat different types of squint, the doctor makes an incision in the membrane that covers the white area of the eye called the conjunctiva. After getting access to the eye muscles, the doctor will either stretch or shorten them for realignment, depending upon the squint type. Squint surgery takes 90 minutes.
In certain types of squint, particularly those that turn inwards, Botox injections are sometimes used as a treatment, as an alternative to surgery. Botulinum toxin, also known as BOTOX, weakens muscles temporarily. It's useful in conditions where it is helpful to weaken muscles to prevent them from pulling the eye and causing it to squint. However, botulinum toxin injections are not commonly used in children.

Vision therapy aims to develop or improve visual skills and abilities. It consists of trained exercises performed over weeks to months with lenses, prisms, patches or balance boards. It focuses on improving visual skills in amblyopia and many binocular vision anomalies. Vision therapies do not correct refractive errors such as myopia. The latest therapy is called ORTHOPTEK EXCECISES and it is highly successful in improving vision and treating squint..
• Orthoptic vision therapy: this is standard vision therapy, focusing on binocular vision and eye movements. It focuses on eye strain, headaches, squints, double vision and reading.
• Behavioral vision therapy or visual integration vision therapy aims to treat problems including difficulties with visual attention and concentration and sometimes it helps in children with attention deficit syndrome.
In adults, the management of squint is different. If it does not improve with glasses, the treatment is surgical. The results of this therapy in adults are not as encouraging as in children, but most patients benefit from the glasses.
• Restoration and correction of vision with glasses, where needed.
• Correction of deviation of eyesight for cosmetic reasons.
• Correction of deviation for functional reasons such as restoration of binocular vision.
• Prevention of double vision
You have to take rest until you recover from the surgery, which could be a few days. Also, initially, you might have to wear glasses for a period of 1 week. You have to avoid swimming for a few weeks.
Treatment of squint and amblyopia at an early stage gives good vision for life. When conservative treatment fails, early surgery should be performed for better visual performance.
A complete eye examination is necessary to avoid any vision threatening complications.
| Week-Days: | 9am - 6pm |
| Sunday: | CLOSED |
Copyright © 2022 · All Rights Reserved Bharti Eye Foundation